Erlang R16B03发布,R17已发力
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自系统技术非业余研究
本文链接地址: Erlang R16B03发布,R17已发力
Erlang R16B03发布了,通常03版本是bug fix版本,进入生产版本,官方的说明如下:
OTP R16B03 is a service release with mostly a number of small corrections and user contributions. But there are some new functions worth mentioning as well, here are some of them:
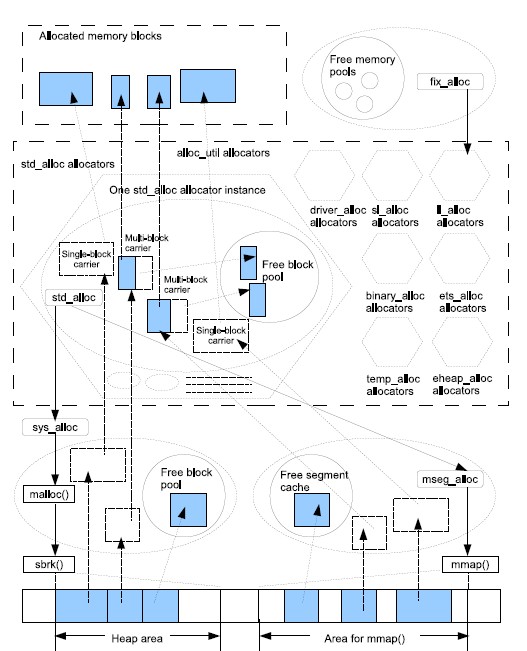
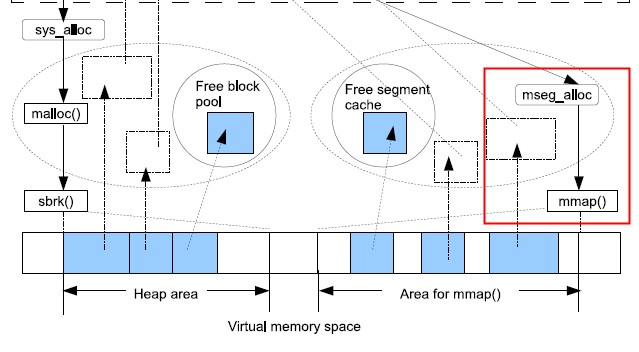
A new memory allocation feature called “super carrier” has been introduced. It can for example be used for pre-allocation of all memory that the runtime system should be able to use. It is enabled by passing the +MMscs (size in MB) command line argument. For more information see the documentation of the +MMsco, +MMscrfsd, +MMscrpm, +MMscs, +MMusac, and, +Mlpm command line arguments in the erts_alloc(3) documentation.
The LDAP client (eldap application) now supports the start_tls operation. This upgrades an existing tcp connection to encryption using TLS, see eldap:start_tls/2 and /3.
The FTP client (inets application) now supports FTP over TLS (ftps).
其中最大的改进就是super carrier, 参见我之前写的博文, 这个特性在于专机专用的系统,内存的使用效率就高很多,同时这个版本对多个核心之间内存倒腾的效率和利用率也高很多,值得大家去用。内存的利用率和碎片率通常不会引起大家的关注,在生产的服务器中,这点非常值得关注。
R16B03发布了后,官方马不停蹄的就进入R17的开发。其中最大的期待就是语言方面的改进,包括eep37和map数据结构。 eep37特性已经进入master, commit在这里, 该特性的具体描述在这里.
简单的说:就是你过去在shell下写如下的fun过去是不可能的。
fun Fact(N) when N > 0 ->
N * Fact(N - 1);
Fact(0) ->
1
end.
但是我们又经常需要这样的匿名函数,比如spawn函数,很不方便。 eep37就是解决这样的事情的。
我们来演示下,首先安装R17:
$ kerl build git git://github.com/erlang/otp.git master r17 && kerl install r17 r17 $ r17/bin/erl Erlang/OTP 17.0-rc0 [erts-6.0] [source-7d4e5e2] [64-bit] [smp:16:16] [async-threads:10] [hipe] [kernel-poll:false] [type-assertions] [debug-compiled] [lock-checking] [systemtap] Eshell V6.0 (abort with ^G) 1> fun Fact(N) when N > 0 -> 1> N * Fact(N - 1); 1> Fact(0) -> 1> 1 1> end. #Fun<erl_eval.29.42696066> 2> F=e(-1). #Fun<erl_eval.29.42696066> 3> F(10). 3628800
eep37这个特性涉及到的改变还是很大的:语言规格,编译器,调试器,dialyzer, tracer, shell, emacs插件等等,全系列的改变,所以要放在R17里面来,虽然看提交,代码早在1年前准备好了。我们再来体验下:
$ cat eep37.erl
-module(eep37).
-compile(export_all).
-spec self() -> fun(() -> fun()).
self() ->
fun Self() -> Self end.
-spec fact() -> fun((non_neg_integer()) -> non_neg_integer()).
fact() ->
fun Fact(N) when N > 0 ->
N * Fact(N - 1);
Fact(0) ->
1
end.
$ r17/bin/erl
Erlang/OTP 17.0-rc0 [erts-6.0] [source-7d4e5e2] [64-bit] [smp:16:16] [async-threads:10] [hipe] [kernel-poll:false] [type-assertions] [debug-compiled] [lock-checking] [systemtap]
Eshell V6.0 (abort with ^G)
1> eep37:fact().
#Fun<eep37.1.16748913>
2> F=e(-1).
#Fun<eep37.1.16748913>
3> F(10).
3628800
4>
小结: 语言也在不停的让用户爽。
祝玩得开心!
Post Footer automatically generated by wp-posturl plugin for wordpress.
Recent Comments