R17新的调度策略+sub
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自系统技术非业余研究
本文链接地址: R17新的调度策略+sub
R17的release note提到:
OTP-11385 A new optional scheduler utilization balancing mechanism has
been introduced. For more information see the +sub command
line argument.Characteristics impact: None, when not enabled. When enabled,
changed timing in the system, normally a small overhead due
to measuring of utilization and calculating balancing
information. On some systems, such as old Windows systems,
the overhead can be quite substantial. This time measurement
overhead highly depend on the underlying primitives provided
by the OS.
引入了新的调度策略,具体的实现参见:这里
作者是大名鼎鼎的rickard-green,代码质量一定不会错的。
那这调度器策略干啥的呢?参见erl文档, 写的很清楚了:
+sub true|false
Enable or disable scheduler utilization balancing of load. By default scheduler utilization balancing is disabled and instead scheduler compaction of load is enabled which will strive for a load distribution which causes as many scheduler threads as possible to be fully loaded (i.e., not run out of work). When scheduler utilization balancing is enabled the system will instead try to balance scheduler utilization between schedulers. That is, strive for equal scheduler utilization on all schedulers.
再对比下默认的调度器策略说明,+scl:
+scl true|false
Enable or disable scheduler compaction of load. By default scheduler compaction of load is enabled. When enabled, load balancing will strive for a load distribution which causes as many scheduler threads as possible to be fully loaded (i.e., not run out of work). This is accomplished by migrating load (e.g. runnable processes) into a smaller set of schedulers when schedulers frequently run out of work. When disabled, the frequency with which schedulers run out of work will not be taken into account by the load balancing logic.
就很容易明白,之前的调度策略是先让低ID的调度器忙起来,不够用的话,再把高ID的拉下水,比较节能。但是在某些专机专用的场合,调度器能耗不是重点,希望全部调度器能够参与计算,减少系统的延迟,才是重点。 那这个+sub true就是你想要的。
这个特性唯一依赖的就是高精度时钟,而linux是不缺的, 默认不开启。
写段代码验证下,fib:busy让CPU保持狂运算:
$ cat fib.erl -module(fib). -export([fib/1, busy/0]). fib(0) -> 1; fib(1) -> 1; fib(N) -> fib(N-1) + fib(N-2). busy()-> fib(10), busy().
分别用不同的调度器策略试验下效果, +sbt db绑定CPU,方便观察:
$ erl +sbt db +sub true Erlang/OTP 17 [erts-6.0.1] [source] [64-bit] [smp:16:16] [async-threads:10] [hipe] [kernel-poll:false] Eshell V6.0.1 (abort with ^G) 1> [spawn(fun()-> fib:busy() end)||_<-lists:seq(1,8)]. [<0.34.0>,<0.35.0>,<0.36.0>,<0.37.0>,<0.38.0>,<0.39.0>, <0.40.0>,<0.41.0>] 2>
不同的策略,CPU使用情况如下图(nmon):
+sub false
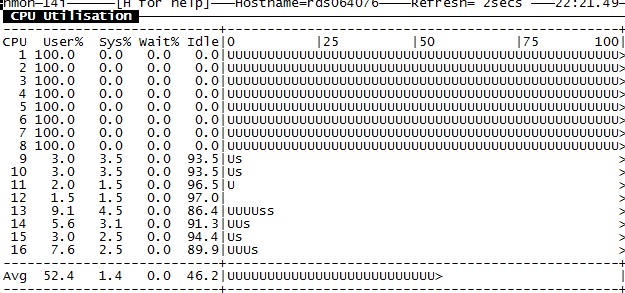
+sub true
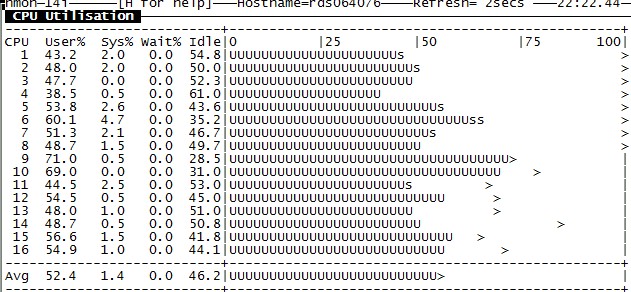
效果非常明显。
祝玩的开心。
Post Footer automatically generated by wp-posturl plugin for wordpress.


Recent Comments