Erlang内存分配器之mbcs_pool
Erlang R17.0 发布的release note 里面花了挺多笔墨讲了内存carrier迁移的特性:
Support for migration of memory carriers between memory allocator instances has been introduced.
By default this feature is not enabled and do not effect the characteristics of the system. When enabled it has the following impact on the characteristics of the system:* Reduced memory footprint when the memory load is unevenly distributed between scheduler specific allocator instances.
* Depending on the default allocaton strategy used on a specific allocator there might or might not be a slight performance loss.
* When enabled on the fix_alloc allocator, a different strategy for management of fix blocks will be used.
* The information returned from erlang:system_info({allocator, A}), and erlang:system_info({allocator_sizes, A}) will be slightly different when this feature has been enabled. An mbcs_pool tuple will be present giving information about abandoned carriers, and in the fix_alloc case no fix_types tuple will be present.For more information, see the documentation of the +M acul command line argument.
那么什么是”migration of memory carriers between memory allocator instances“,解决什么问题呢?
官方的文档 erts/emulator/internal_doc/CarrierMigration.md, 见这里, 已经描述的非常清楚了。
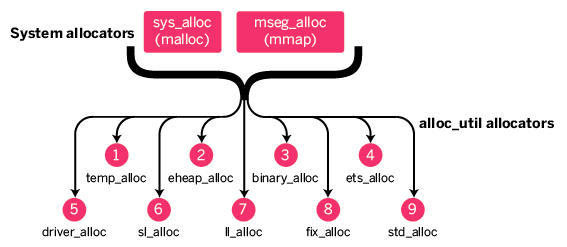
我来简单的说下复述下:
Erlang的内存分配器为了提高性能,每个调度器一个都有自己的内存池,在申请/释放内存的可以避免大量的锁争用,提高了性能。但也带来内存浪费的问题,首先调度器默认使用策略是“full load or not”, 也就是说低ID的调度器如果没饱和的话,不会用下一个调度器。在高负载的情况下,更多的调度器被启用,该调度器上的内存被缓冲,留在池子里。当工作负载下去的的话,因为压力没到,高ID的调度器没机会被使用,也就是说这个时候,这个调度器上的内存就浪费掉了,从整个VM的角度来看,内存的碎片率就很高。Erlang的VM是以稳定性著名的,但是它也有Crash的时候,十有八九是因为内存爆了。我们在设计系统的时候,通常从数据量去反推需要的内存,但是如果有碎片或者浪费存在严重的话,我们就无法准确,就可能导致灾难。 为了解决这个问题,最直接的反应就是当每个调度器池子里面的内存使用率低于一定程度的时候,就把该块内存出让出来,让有需要的调度器能够利用起来。这就是内存carriers迁移要解决的核心问题。
这个特性在R16加入的默认不启用,R17默认启用了,也就是说+M acul 默认是“de”. 带来的影响有下面几个:
1. 内存申请的效率,现在的测试是先在自己的池子里面分配,不满足了就找cpool,再不满足才去找mseg或者sys分配器申请。效率和利用率是鱼和熊掌不可兼得。
2. 内存分配器的内存除了在池子里面还有在cpool里,统计内存的时候要小心。
3. 内存浪费率到什么时候被废弃。

Recent Comments