Erlang集群RPC通道拥塞问题及解决方案
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自系统技术非业余研究
本文链接地址: Erlang集群RPC通道拥塞问题及解决方案
Erlang的集群默认情况下是全联通的,也就是当一个节点加入集群的时候,介绍人会推荐集群里面所有的节点主动来和新加入的节点建立联系,
效果如下图:
我们这次不讲如何避免全联通而是来讲这个节点间通道的问题。
我们知道erlang的消息发送是透明的,只要调用Pid!Msg, 虚拟机和集群的基础设施会保证消息到达指定的进程的消息队列,这个是语义方面的保证。那么如果该Pid是在别的节点,这个消息就会通过节点间的rpc通道来传递。rpc模块就是基于erlang的这个语义在上面实现了远程函数调用。
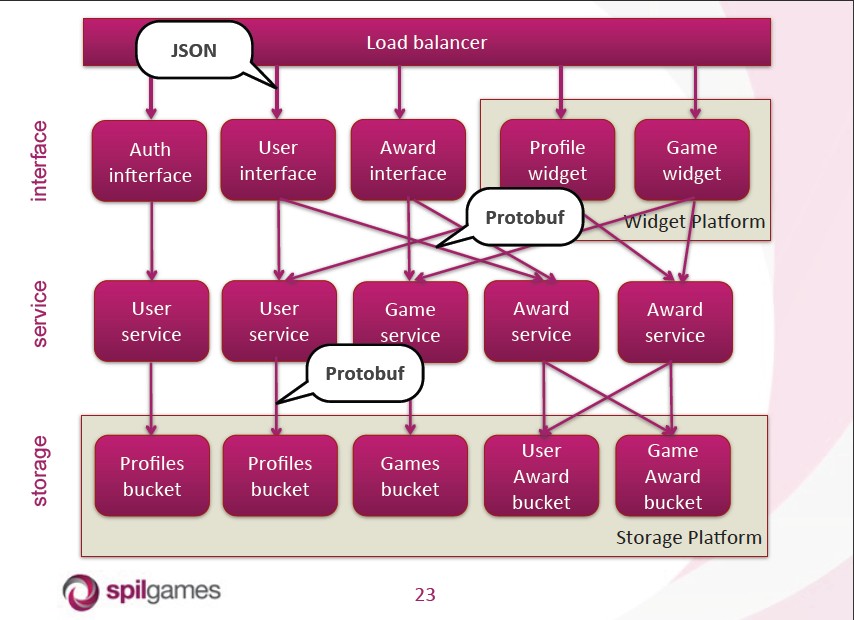
目前社区推比较推荐erlang服务分层,所以层和层之间的交互基本上透过rpc来进行的。类似下图的分层结构越来越多,当大量的消息在节点间流动的话,势必会造成通道拥塞。
阻塞会导致发送进程被挂起,而rpc是单进程(gen_server)的,被挂起,rpc调用就废了。当然除了RPC, Pid!Msg 这种方式还是可以并行的走的。
这种阻塞极大的影响力系统的rt, 对性能和体验有很大的影响。
那这个问题如何定位、解决呢?Erlang很贴心的提供了一揽子解决方案:
首先是发现问题:
erlang:system_monitor(MonitorPid, Options) -> MonSettings
busy_dist_port
If a process in the system gets suspended because it sends to a process on a remote node whose inter-node communication was handled by a busy port, a message {monitor, SusPid, busy_dist_port, Port} is sent to MonitorPid. SusPid is the pid that got suspended when sending through the inter-node communication port Port.
比如说 riak_sysmon 就用了以下代码:
BusyDistPortP = get_busy_dist_port(),
Opts = lists:flatten(
[[{long_gc, GcMsLimit} || lists:member(gc, MonitorProps)
andalso GcMsLimit > 0],
[{large_heap, HeapWordLimit} || lists:member(heap, MonitorProps)
andalso HeapWordLimit > 0],
[busy_port || lists:member(port, MonitorProps)
andalso BusyPortP],
[busy_dist_port || lists:member(dist_port, MonitorProps)
andalso BusyDistPortP]]),
_ = erlang:system_monitor(self(), Opts),
当我们收到{monitor, SusPid, busy_dist_port, Port}消息的时候,就可以确认系统经常有阻塞问题。
那么如何解决呢?
社区早就认识到这个问题, 所以设计dist_buf_busy_limit是个可配置的值。
我们需要先知道我们的系统是什么情况:
从 http://www.erlang.org/doc/man/erlang.html#system_info_dist_buf_busy_limit 摘抄如下:
erlang:system_info(Item :: dist_buf_busy_limit) -> integer() >= 0
dist_buf_busy_limit
Returns the value of the distribution buffer busy limit in bytes. This limit can be set on startup by passing the +zdbbl command line flag to erl.
我们来演示下:
$ erl Erlang R16B (erts-5.10.1) [source] [64-bit] [smp:16:16] [async-threads:10] [hipe] [kernel-poll:false] Eshell V5.10.1 (abort with ^G) 1> erlang:system_info(dist_buf_busy_limit). 1048576 2>
默认情况下是1M,一般情况下是够用了,但是如果你的rpc没设计好返回大量的数据,这个值就可能不够了。
我们可以通过修改这个值来回避这个问题:
从 http://www.erlang.org/doc/man/erl.html#+zdbbl 摘抄如下:
+zdbbl size
Set the distribution buffer busy limit (dist_buf_busy_limit) in kilobytes. Valid range is 1-2097151. Default is 1024.A larger buffer limit will allow processes to buffer more outgoing messages over the distribution. When the buffer limit has been reached, sending processes will be suspended until the buffer size has shrunk. The buffer limit is per distribution channel. A higher limit will give lower latency and higher throughput at the expense of higher memory usage.
需要注意的是它的单位是K。
社区也碰到很多这样的问题,比较典型的就是riak自己,参看这篇 文章
The important takeaway here is to check your Riak logs for busy_dist_port warnings and take them seriously.
A simple addition of the line +zdbbl 8192 to Riak’s vm.args to bump the Erlang distribution channel buffer size to 8MB from the default of 1MB is all it took to realize all of the benefits discussed thus far.
小结: 发现问题,解决问题,需要有测量和数据。
祝玩得开心!
Post Footer automatically generated by wp-posturl plugin for wordpress.
好文,谢谢分享。